
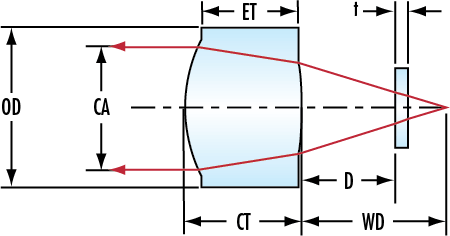
LightPath® Geltech™ Molded Aspheric Lenses are used to eliminate spherical aberration and improve focusing and collimating accuracy in a variety of laser applications. Low NA aspheric lenses are designed to maintain beam shape, while high NA lenses gather all available light to maintain beam power over long distances. LightPath® Geltech™ Molded Aspheric Lenses are ideal for applications including sighting systems, bar code scanners, laser diode-to-fiber coupling, optical data storage, or biomedical lasers.
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2024, Edmund Optics Singapore Pte. Ltd, 18 Woodlands Loop #04-00, Singapore 738100
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act
The FUTURE Depends On Optics®