
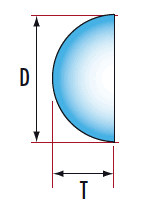
Sapphire and Ruby Half-Ball Lenses feature a very short back focal length with the convenience of a flat surface for easy mounting. Sapphire features a high index of refraction and excellent broadband transmission characteristics. Ruby half-ball (hemispherical) lenses are easier to see and, therefore, easier to handle for physical applications. Sapphire and Ruby Half-Ball Lenses are very chemically stable and are great for severe environments, high-temperature applications, and applications requiring high melting points. Typical applications include fiber communication, endoscopy, microscopy, optical pick-up devices, and laser measurement systems.
1-800-363-1992
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2025, Edmund Optics Singapore Pte. Ltd, 18 Woodlands Loop #04-00, Singapore 738100
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act