
Posts and Post Holders are required for mounting to a breadboard.
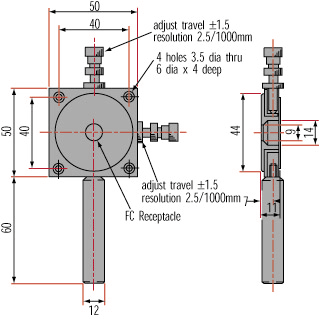
Fiber Optic Alignment Mounts can translate optical fibers terminating in an FC connection. Useful for telecom positioning and for aligning FC Fiber Optic Patchcords, they feature ±1.5mm travel in both the X and Y-axis. The Differential Micrometer models feature 2.5 micron resolution while the kinematic version (#55-478) provides an additional ±2° tilt adjustment on each axis.
Note: Posts and Post Holders are required for mounting to a breadboard.
1-800-363-1992
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2025, Edmund Optics Singapore Pte. Ltd, 18 Woodlands Loop #04-00, Singapore 738100
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act